What is the Bitcoin Lightning Network? Exploring the Future of Scalable and Instantaneous Bitcoin Transactions

Introduction
In recent years, Bitcoin has captured the imagination of individuals, businesses, and investors worldwide. As its popularity soars, the need for scalable solutions becomes increasingly crucial. Enter the Bitcoin Lightning Network—a groundbreaking innovation that promises to revolutionize Bitcoin transactions by addressing scalability and transaction speed limitations. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the Lightning Network, explore its inner workings, highlight its advantages, discuss potential use cases, address its challenges, and compare it with other scaling solutions. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unlock the transformative power of the Bitcoin Lightning Network.
Understanding the Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Concept of the Lightning Network
The Lightning Network serves as a layer-2 solution that addresses the scalability challenges of Bitcoin. By operating on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, it introduces a network of payment channels that enable off-chain transactions.
Creating Payment Channels
Payment channels are created by participants who lock up a certain amount of Bitcoin in a multi-signature wallet. This establishes a secure and trustless environment for conducting transactions. Payment channels act as conduits for off-chain transactions, reducing congestion on the main blockchain.
Facilitating Off-Chain Transactions
With payment channels in place, participants can engage in an unlimited number of off-chain transactions without burdening the main blockchain. These transactions occur instantly and with minimal fees. The Lightning Network leverages the security and immutability of the underlying blockchain while providing lightning-fast transaction speeds.
The Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts play a vital role in the Lightning Network’s functionality. They ensure integrity and enforce the terms of transactions within the payment channels. Through programmable rules, smart contracts enable secure and trustless interactions between participants. They facilitate the automatic execution of transactions, dispute resolution, and the net settlement of final channel states on the Bitcoin blockchain.
By combining layer-2 technology, payment channels, and smart contracts, the Lightning Network achieves scalability and enables efficient off-chain transactions, revolutionizing the way Bitcoin is transacted.
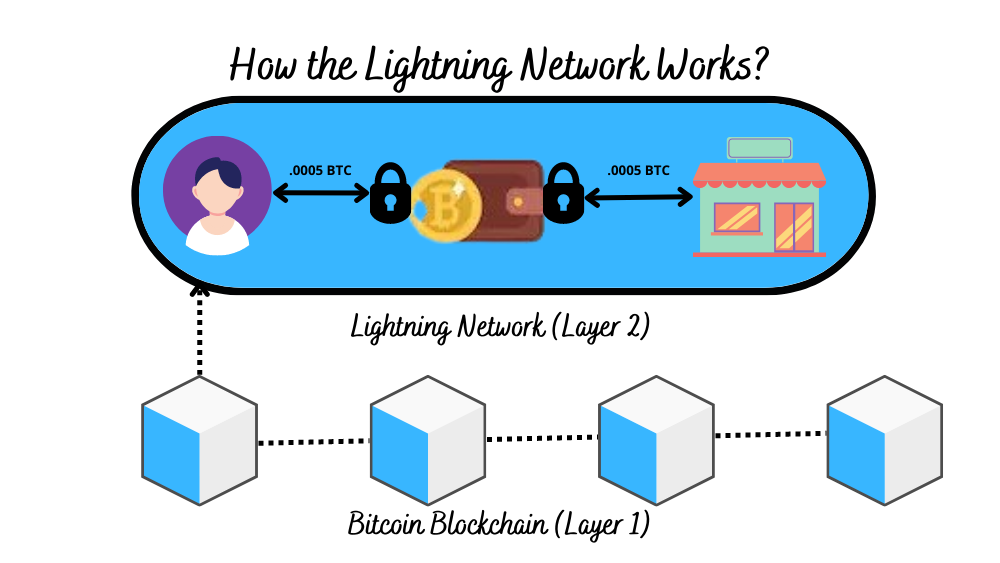
How Does the Bitcoin Lightning Network Work?
Opening and Closing Payment Channels
To utilize the Lightning Network, participants must open payment channels. Opening a payment channel involves creating a multi-signature wallet on the Bitcoin blockchain, where participants lock up a certain amount of Bitcoin. This initial transaction is recorded on the blockchain, establishing the starting state of the payment channel.
Once the payment channel is open, participants can conduct off-chain transactions with each other. These transactions are not immediately broadcasted to the blockchain, enabling fast and low-cost transactions between the participants. They can continue to transact freely until they decide to close the payment channel.
Closing a payment channel involves settling the final state of the channel on the blockchain. The net balance of all transactions that occurred within the payment channel is reflected in the closing transaction. By doing so, participants ensure that the correct ownership of Bitcoin is maintained, and any disputes or discrepancies are resolved.
Routing Payments Through Intermediary Nodes
The Lightning Network allows users to send payments to other participants even if they don’t have a direct payment channel with them. This is made possible by routing payments through intermediary nodes. These nodes act as bridges, facilitating transactions between participants who are not directly connected to the Lightning Network.
Routing payments involves finding a path of connected payment channels between the sender and the recipient. Each channel along the route contributes to forwarding the payment until it reaches its destination. The Lightning Network protocol uses sophisticated algorithms to find the most efficient and cost-effective routes for payment routing.
Setting up a Lightning Network node or opening a payment channel requires a step-by-step process:
- Choose a compatible Lightning Network implementation, such as LND or c-lightning.
- Install and configure the Lightning Network software on your device.
- Establish connections with other Lightning Network nodes to form a network.
- Fund your Lightning Network wallet by sending Bitcoin to a multi-signature address.
- Open a payment channel with another participant by committing funds to the channel.
- Once the channel is open, you can start transacting with other participants on the Lightning Network.
Multi-Signature Transactions for Security and Dispute Resolution
Security is a fundamental aspect of the Lightning Network. Multi-signature transactions play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of off-chain transactions. In a payment channel, multi-signature addresses require multiple signatures from participants to execute a transaction. This mechanism prevents any single participant from unilaterally spending the funds in the channel without the consent of the other participants.
In case of disputes or disagreements between participants, the Lightning Network leverages the power of multi-signature transactions for dispute resolution. By using time-locked transactions, participants have a specific window of time to provide a valid transaction that reflects the correct channel state. If one participant tries to cheat or broadcast an incorrect transaction, the other participant can use the latest valid transaction to close the channel and safeguard their funds.
By utilizing multi-signature transactions, the Lightning Network enhances the security of off-chain transactions, provides a mechanism for trustless interactions, and ensures that participants have control over their funds.
Understanding the process of opening and closing payment channels, routing payments through intermediary nodes, and the use of multi-signature transactions is essential to grasp the inner workings of the Lightning Network and its ability to enable fast, secure, and scalable transactions on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
You may like How to Buy Crypto with Gift Card and Sell for Bitcoin Instantly
Advantages of the Bitcoin Lightning Network
Scalability
The Lightning Network offers a scalable solution to the inherent transaction throughput limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain. By conducting off-chain transactions through payment channels, the Lightning Network significantly increases the potential transaction capacity. It enables a high volume of fast and low-cost transactions to occur without burdening the main blockchain. As more participants join the Lightning Network, its scalability potential grows exponentially, allowing for widespread adoption and global transaction scalability.
Reduced Transaction Fees and Cost-effectiveness
One of the key advantages of the Lightning Network is its ability to reduce transaction fees associated with on-chain Bitcoin transactions. As off-chain transactions occur within payment channels, they are not subject to the fees imposed by the Bitcoin network. Transaction fees on the Lightning Network are typically minimal or even negligible, making microtransactions economically viable. This reduction in fees makes the Lightning Network a cost-effective solution for everyday transactions, particularly for small-value payments that would be impractical to execute directly on the blockchain.
Instant Settlement and Real-world Implications
Off-chain transactions conducted through the Lightning Network offer an instant settlement, providing a seamless user experience for everyday Bitcoin transactions. Unlike traditional on-chain transactions that require confirmations on the blockchain, Lightning Network transactions can be completed in a matter of seconds. This opens up possibilities for various real-world applications, such as point-of-sale transactions, online purchases, and even machine-to-machine interactions.
For example, imagine a coffee shop accepting Bitcoin payments through the Lightning Network. A customer can simply scan a QR code, initiate the payment, and instantly settle the transaction, allowing them to receive their coffee without delay. This near-instantaneous settlement creates a user-friendly experience compared to traditional payment methods, while still leveraging the security and benefits of Bitcoin.
Successful Lightning Network implementations have been observed in various real-world scenarios. For instance, the gaming industry has embraced the Lightning Network to enable microtransactions within games, allowing players to make small in-game purchases without incurring high fees. Additionally, content creators and artists have utilized the Lightning Network for direct payments, enabling fans to support their favorite creators with small donations instantly.
These real-world examples and case studies highlight the practical applications and the potential for widespread adoption of the Lightning Network in everyday Bitcoin transactions. The instant settlement feature enhances efficiency, convenience, and usability, further propelling the adoption of the Lightning Network.
The Bitcoin Lightning Network’s advantages in scalability, reduced transaction fees, and instant settlement present a compelling case for its adoption and utilization. By addressing the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain, the Lightning Network offers a transformative solution that enables efficient and cost-effective Bitcoin transactions in various contexts.
You may like How to Profit from Bitcoin Price Fluctuations in 2023
Potential Use Cases and Applications
Microtransactions and Everyday Purchases
The Lightning Network opens up new possibilities for microtransactions, which are small-value transactions that were previously impractical due to high transaction fees on the Bitcoin blockchain. With its reduced fees and instant settlement feature, the Lightning Network is ideal for facilitating microtransactions. This has significant implications for various industries, such as gaming, content creation, digital media, and online services. For instance, users can pay small amounts to access premium content, make in-app purchases, or support their favorite content creators with micro-donations. The Lightning Network enables frictionless and cost-effective transactions for everyday purchases, making Bitcoin a viable currency for day-to-day transactions.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine Transactions
The Lightning Network’s ability to facilitate fast and low-cost transactions make it suitable for the Internet of Things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) interactions. With the increasing proliferation of IoT devices, there is a need for seamless and secure transactions between these devices. The Lightning Network can enable autonomous machines to conduct microtransactions and settle payments instantly. For example, a smart car could pay for parking or tolls in real-time, or a vending machine could automatically restock itself by purchasing inventory from suppliers using Lightning Network transactions. By integrating the Lightning Network with IoT devices, a new world of automated and efficient transactions becomes possible.
Cross-Border Transactions and Remittances
Cross-border transactions and remittances often involve high fees, long processing times, and various intermediaries. The Lightning Network has the potential to revolutionize this space by enabling fast, secure, and cost-effective cross-border transactions. With its instant settlement and reduced fees, the Lightning Network offers an alternative to traditional remittance methods, which are often expensive and time-consuming. By leveraging the Lightning Network, individuals can send and receive cross-border payments with minimal fees and near-instant transaction times, enhancing financial inclusivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, the Lightning Network’s ability to route payments through intermediary nodes makes it particularly beneficial for cross-border transactions. It allows participants to connect with multiple payment channels, creating a network effect that increases liquidity and accessibility. This enables seamless and efficient transfer of value across different currencies, potentially reducing the reliance on traditional banking systems for cross-border payments.
By exploring the potential of the Lightning Network in microtransactions, everyday purchases, IoT, machine-to-machine transactions, cross-border transactions, and remittances, we can envision a future where Bitcoin transactions are not only scalable and efficient but also deeply integrated into various aspects of our lives. The Lightning Network’s transformative capabilities have the potential to reshape industries and create new opportunities for innovation and financial inclusion.
Challenges and Limitations of the Lightning Network
Liquidity Constraints and Channel Capacity
One of the current challenges facing the Lightning Network is liquidity constraints. To facilitate transactions on the Lightning Network, participants need to have sufficient funds locked in payment channels. However, liquidity can be limited, especially in less active channels or for participants with smaller amounts of Bitcoin. This can hinder the ability to route payments effectively and may require participants to actively manage their channels to maintain sufficient liquidity.
Another related limitation is the channel capacity, which refers to the maximum amount of Bitcoin that can be transacted within a payment channel. The capacity of a channel is determined by the initial funding amount. If a channel’s capacity is reached, additional funds cannot be added unless the channel is closed and a new one is opened. Channel capacity limitations can impact the size and value of transactions that can be conducted on the Lightning Network.
Efforts are being made to address these challenges. Improvements in routing algorithms, liquidity management tools, and techniques to incentivize participants to maintain open channels are being developed. Additionally, solutions like “watchtowers” are being explored to enhance channel capacity and liquidity management, ensuring a more seamless and efficient Lightning Network experience.
Security and Trust in Off-chain Transactions
While the Lightning Network incorporates various security measures, there are concerns related to the trustworthiness and security of off-chain transactions. As Lightning Network transactions occur off-chain, there is a level of trust required between participants. Participants need to ensure that their channel partners will not attempt to cheat or broadcast incorrect transactions. Although mechanisms like multi-signature transactions and time-locked transactions provide security and dispute resolution, the possibility of malicious behavior remains a concern.
To address these concerns, ongoing development efforts focus on improving security measures and enhancing the trustless nature of Lightning Network transactions. Research is being conducted on mechanisms like “justice transactions” that allow participants to punish dishonest behavior and ensure fair channel settlements. Additionally, advancements in cryptographic protocols and smart contract technology are being explored to enhance the security and trustworthiness of off-chain transactions.
Ongoing Development Efforts and Potential Solutions
The Lightning Network is a dynamic and evolving technology and ongoing development efforts are dedicated to overcoming its challenges and limitations. The Lightning Network community, developers, and researchers are actively working on potential solutions to enhance the scalability, usability, and security of the network.
Efforts are focused on improving routing algorithms to optimize the efficiency and reliability of payment routing. Solutions like “trampoline payments” are being explored to enable more efficient routing across the network, reducing the need for direct channels between participants. Additionally, advancements in user experience, such as simplified channel management and intuitive wallet interfaces, are being developed to make the Lightning Network more accessible to a broader user base.
Interoperability between different Lightning Network implementations is another area of focus. The development of standards and protocols that ensure compatibility and seamless communication between different Lightning Network nodes and wallets would foster network growth and enhance the overall user experience.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development aim to address the challenges of liquidity constraints and channel capacity. Techniques like atomic multipath payments and submarine swaps are being explored to enhance liquidity and increase the capacity of payment channels. These innovations would enable more robust and scalable Lightning Network transactions.
Comparison with Other Scaling Solutions
When it comes to scaling solutions for blockchain networks, the Lightning Network is just one option among several others, including on-chain scaling and sidechains. Each approach offers its own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different use cases. Let’s compare and contrast these scaling solutions.
1. Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a layer-2 solution built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. It enables off-chain transactions through the use of payment channels, allowing participants to conduct fast and low-cost transactions without burdening the main blockchain. Here are the key advantages and disadvantages of the Lightning Network:
Advantages:
- Scalability: The Lightning Network provides a scalable solution by enabling a high volume of transactions to occur off-chain, alleviating the transaction throughput limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Reduced Fees: Off-chain transactions on the Lightning Network come with minimal fees, making microtransactions economically viable.
- Instant Settlement: Transactions on the Lightning Network can be settled almost instantly, providing a seamless user experience.
- Privacy: The Lightning Network offers a higher level of privacy compared to on-chain transactions, as not all transactions are broadcasted to the public blockchain.
Disadvantages:
- Liquidity Constraints: Liquidity can be a challenge, especially for less active channels or participants with smaller amounts of Bitcoin.
- Channel Capacity: The maximum capacity of a payment channel can limit the size and value of transactions.
- Trust Requirements: Participants in the Lightning Network need to trust each other to ensure the security and integrity of off-chain transactions.
The Lightning Network is well-suited for use cases that require fast and frequent transactions, such as microtransactions, everyday purchases, and cross-border transactions. It offers a balance between scalability, low fees, and instant settlement, making it suitable for scenarios where speed and efficiency are crucial.
2. On-chain Scaling
On-chain scaling focuses on increasing the capacity of the blockchain itself, allowing for more transactions to be processed directly on the main chain. This approach involves making changes to the blockchain’s protocol and consensus mechanisms. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of on-chain scaling:
Advantages:
- Simplicity: On-chain scaling doesn’t require additional infrastructure or complex payment channel setups. It relies on the existing blockchain structure.
- Decentralization: On-chain scaling preserves the decentralized nature of the blockchain by ensuring that all transactions are processed and validated by network participants.
Disadvantages:
- Scalability Challenges: On-chain scaling faces inherent limitations due to factors such as block size restrictions and transaction processing times.
- Increased Costs: As the blockchain grows in size, the cost of running a full node and validating transactions may become more resource-intensive.
- Potential Centralization: Large block sizes and increased resource requirements could lead to centralization, as only entities with significant resources can participate in block validation.
On-chain scaling is suitable for use cases that prioritize maximum decentralization and security over transaction speed. It ensures that all transactions are processed on the main blockchain, but scalability challenges may arise as the network grows, potentially leading to higher fees and longer confirmation times.
3. Sidechains
Sidechains are separate chains linked to the main blockchain, allowing for the execution of different protocols and the development of specific use cases. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of sidechains:
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Sidechains enable the development and implementation of custom protocols and features that may not be feasible or appropriate for the main blockchain.
- Scalability: By offloading certain types of transactions to sidechains, the main blockchain’s capacity can be preserved for high-value or critical transactions.
- Interoperability: Sidechains can facilitate interoperability between different blockchain networks, enabling seamless transfer of assets and data.
Disadvantages:
- Security Considerations: Sidechains introduce additional security risks, as they rely on separate consensus mechanisms and may have different levels of decentralization and security compared to the main blockchain.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing sidechains can be more complex than other scaling solutions, requiring additional development and infrastructure.
Sidechains are suitable for use cases that require specialized functionality or specific protocols that may not be feasible or practical on the main blockchain. They offer scalability and flexibility, allowing for the execution of diverse applications while maintaining interoperability with the main blockchain.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin Lightning Network holds immense potential to revolutionize Bitcoin transactions. With its scalability, reduced fees, and instant settlement features, it addresses the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain and enables faster and more scalable transactions. We encourage readers to explore and experiment with the Lightning Network, as it offers a transformative solution for unlocking the full potential of Bitcoin. By embracing this technology, users can experience the benefits firsthand and contribute to the growth and development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
FAQs
A1. The Lightning Network utilizes a combination of smart contracts, cryptographic techniques, and network consensus to ensure the security of off-chain transactions. Multi-signature transactions and penalty mechanisms protect against fraudulent behavior. Additionally, the network’s decentralized nature and payment channel mechanisms enable trustless and secure transactions.
A2. Yes, although the Lightning Network was initially developed for Bitcoin, its concept can be extended to other compatible cryptocurrencies. Several cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin, have already implemented their own versions of the Lightning Network. However, cross-chain compatibility and liquidity may vary across different implementations.
A3. No, in order to receive payments on the Lightning Network, it is necessary to have an open payment channel. Opening a payment channel allows users to transact with other participants on the Lightning Network and receive payments. Each participant must have an open channel to actively engage in Lightning Network transactions.
A4. Merchants can benefit from adopting the Lightning Network for Bitcoin payments in several ways. First, it offers faster transaction confirmations, allowing for seamless and efficient customer experiences. Second, the reduced transaction fees on the Lightning Network can significantly lower the costs associated with accepting Bitcoin payments. Lastly, by leveraging the Lightning Network, merchants can tap into the growing user base and popularity of this scalable solution, attracting Bitcoin users who value speed and cost-effectiveness.
A5. There are several popular Lightning Network wallets available, each with its own unique features and user interfaces. Some notable examples include:
- Eclair Wallet: This wallet is available for Android devices and allows users to send and receive Lightning Network payments easily.
- BlueWallet: Available for both iOS and Android, BlueWallet supports both on-chain Bitcoin transactions and Lightning Network payments, providing a seamless experience.
- Zap Wallet: Zap is a popular Lightning Network wallet available for desktop and mobile platforms. It offers a user-friendly interface and advanced features such as autopilot routing and channel balancing.


