What is ETH 2.0?
Ethereum network is one of the largest and most widely used blockchain networks in the world with a market capitalization of $26,628,563,991. Since the launch in 2015, Ethereum has been making headways to achieving its ultimate goal of becoming a decentralized global computer, that would someday take over centralized applications used in daily activities. However, the community still has a lot of work to do in accomplishing this goal.
When Ethereum was launched, its long-term roadmap was divided into four stages:
- Frontier: Released in 2015, it was the first live version of the network that enabled users to mine Ether, build Dapps, tools, and experiment on its platform.
- Homestead: Homestead was released in 2016 and was the first production release of Ethereum blockchain. It increased transaction speed on the network and improved many protocols that will be used in the foundation for future upgrades.
- Metropolis: This is the third and current stage of Ethereum’s development. It is divided into two releases, Byzantium and Constantinople. Byzantium was first released in 2017 and was known to be the lighter, faster and a more secure version than the previous one. It improved privacy, other upgrades include predictable gas prices and easier programming.
- Constantinople: Constantinople was released on February 28, 2019, with the goal to further build the improvements in the previous stages.
- Ethereum 2.0 or Serenity: This upgrade is meant to improve every aspect of the Ethereum network. The new development, Ethereum 2.0, will be addressing major issues that the Ethereum network faces currently. The issues of scalability, efficiency and speed. To the Ethereum network, Ethereum 2.0 will not be introduced as a hard fork rather, its users can transfer value from its current Proof-of-work (PoW) chain via a one-way smart contract into the new

What is Ethereum 2.0 (Serenity)?
Serenity is a new block chain with a link to the existing POW chain. Therefore, POS chain is aware of the block hashes of proof of work chain so you can move your ether from POW to POS chain. As earlier stated, it’s the final stage of the Ethereum’s development which will be solving major problems that the network faces currently.
Ethereum 2.0 specification is divided into two chains.
- The Beacon Chain
- The Shard Chain
The Beacon Chain
With no clarity about the outcome of proof of stake and sharding, Casper FFG and coredev realized that it would be profitable to combine Proof of Stake and the sharding together in the beacon chain architecture.
The Beacon chain is the base of the sharding system and the system chain at the core of Ethereum 2.0 accompanied with some responsibilities.
Here are the main responsibilities of the beacon chain:
- Storage and maintenance of the registry for validators
- Cross-links processing
- Processing its own block-by-block consensus and the finality gadgets
Who is a Validator?
A Validator is one who deposits a pile of ETH into smart contracts. in order to participate In Ethereum’s consensus algorithm, the Validator runs a node that signs coins with the same key that controls the deposited ETH and keeps the network running. A validator is a member of the Casper / sharding consensus system that is very much like a node or the miner of ‘Proof of Work’ protocol that is allowed to be engaged in the process when a security deposit is made.
Ethereum “Serenity” upgrade is designed to pay validators to secure the network rather than paying miners. To become an active validator, you must deposit 32 ETH into the Casper mechanism, the beacon chain processes deposit-transaction receipts, reaches an activation balance then begins a queuing process.
The profitability of a Validator is dependent on his/her online availability. Beacon chain’s primary source of load is attestations. These attestations are concurrently proof of stake votes for Beacon chain block and also availability votes for Shard blocks and a cross-link is created when there’s a sufficient number of attestations for a particular shard block.
What is cross-link?
Cross-link is a set of signature from a board attesting to a block in a shard chain. They serve as the main source by which beacon chain stay updated about the state of shard chains.
What is a Shard Chain?
A Shard Chain is one of the chains where user transactions are carried out and the account data is stored. This phase deals with the construction, validity, and consensus on the data of the shard chains. There is no indication of state execution or account balances. Shard Data Chain outweighs the Python proof-of-concept implementation and displays current spec changes. However, it’s still a work-in-progress for researchers and implementers.
The introduction of Sharding should remove the most significant problem for transaction speed and would be the best solution for scalability. Also, off-chain solutions like plasma chains and state channels will likely be used to minimize the workload on the main network and also increase scalability.
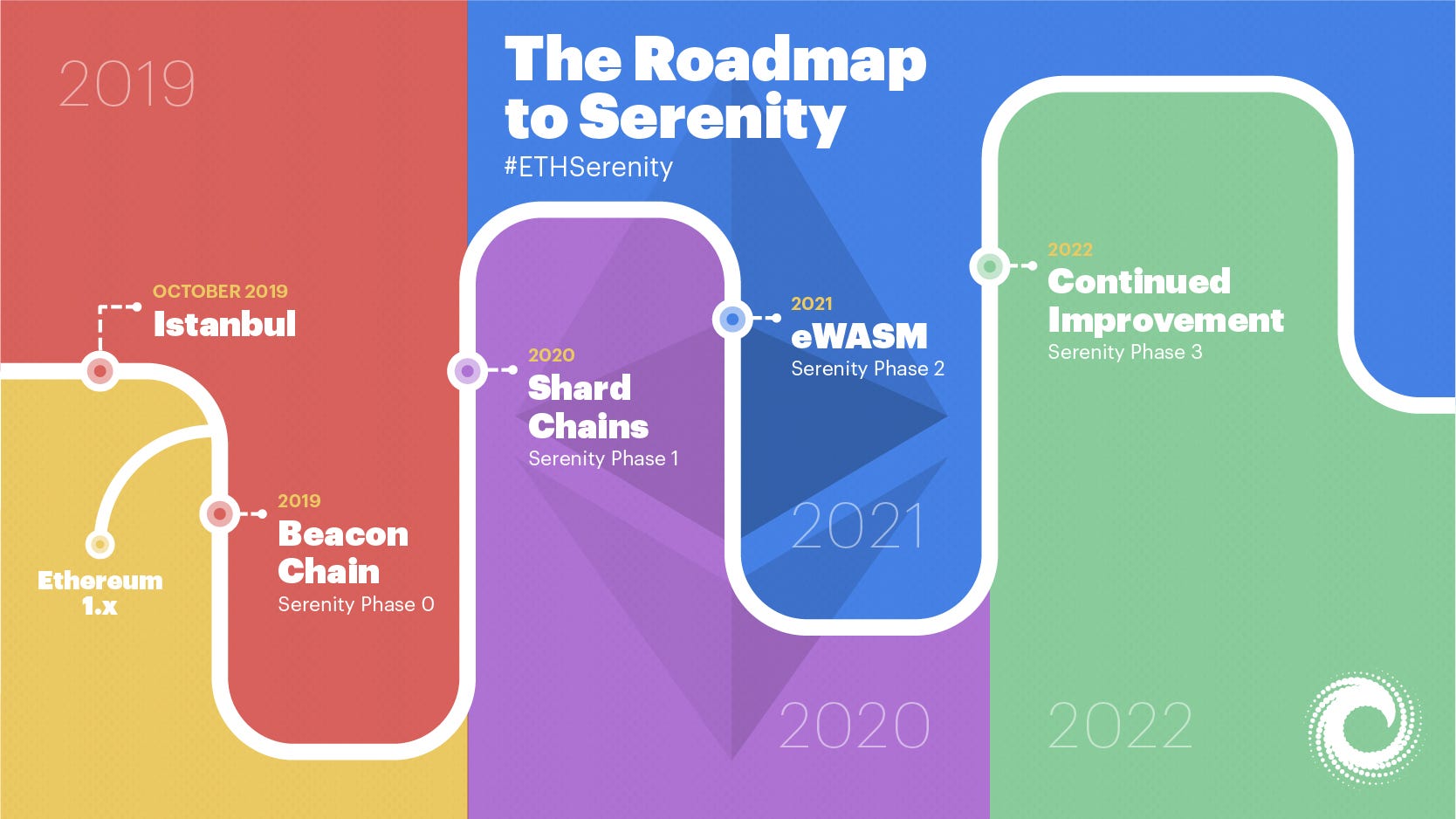
Will EWASM replace EVM?
Another major problem that Ethereum 2.0 will be solving as earlier stated is speed and usability.
The EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) is the key structure of the Ethereum network that executes codes and causes the network to function properly. It is responsible for the network’s computations and ensures accurate account information such as balances, block information, addresses, and current gas prices. The machine handles all Ethereum smart contracts written in solidity which are then compiled into unique EVM bytecode. These contracts are executed by each node on the network. EVM also keeps track of the following components; Block information, storage state, account state, and runtime environment.
Due to the many responsibilities, the Virtual Machine executes, the speed at which the machine performs tasks has a major effect on the general speed and functionality of the network. Thus Ethereum 2.0 has devised an advanced solution called EWASM (Ethereum-flavored Web Assembly).
The WASM is a W3C group open standard instruction-set developed by engineers from Google, Mozilla, Microsoft, and Apple. Aside from solving the problem of speed and usability, it will also increase the security of the Ethereum network.
In addition, other goals of Ethereum 2.0 will involve reducing network complexity even if it will lead to a few losses in efficiency. Another goal is to make use of cryptography and design techniques for the involvement of a large set of validators, in per and total transactions and so much more.
Coincola is excited about the new development and can’t wait for its launch. We believe this will onboard new users to the Ethereum network. However, till then, visit our website, create an account and start to purchase or trade your ETH at a cheap rate and on a fast and secure platform.



